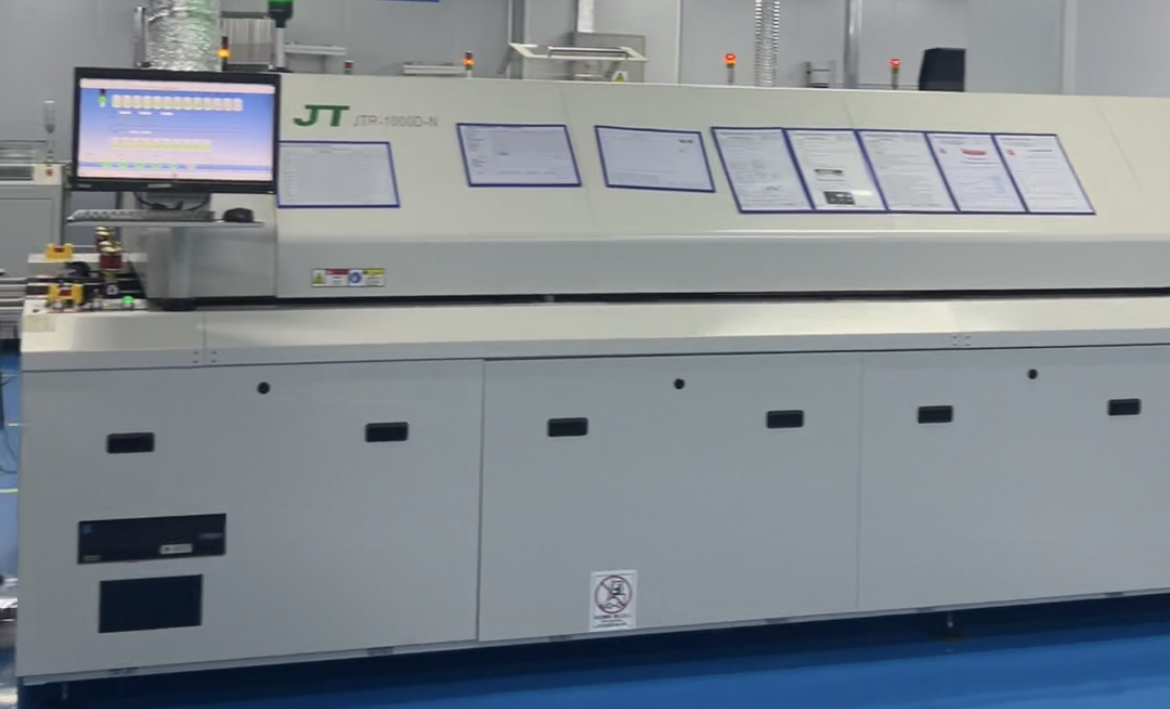
Before starting assembly, in what situations is it necessary to bake the PCB?
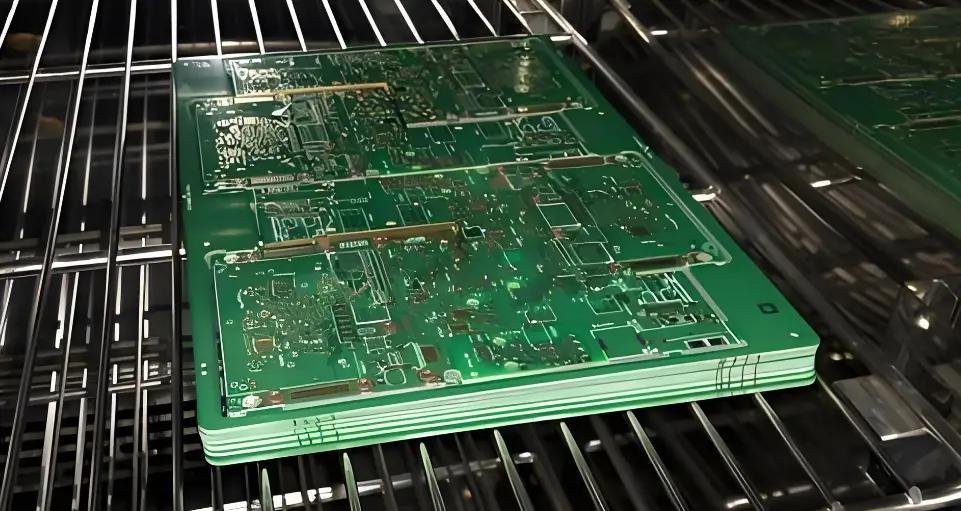

The main scenarios are as follows:
1. Storage time and placement after opening exceeding regulations: PCBS manufactured within 2 months and well sealed should be placed in an environment of ≤30℃/60%RH for more than 5 days after opening. PCBS stored for 2 to 12 months; PCBS that have been stored for more than 12 months but have to be used all need to be baked for the corresponding duration before assembly.
2. Moisture or damage to the packaging: If the vacuum packaging is damaged or the humidity indicator card inside the packaging shows that it is damp, even if the storage time is short, it needs to be baked to dehumidify to prevent moisture from remaining inside.
3. Special boards or special structure PCBs: Multi-layer boards and HDI boards are prone to residual lamination moisture. High-frequency boards absorbing moisture can affect the dielectric constant, and flexible boards absorbing moisture can cause copper foil peeling. Such PCBS usually need to be baked before assembly, and the baking temperature for flexible boards and the like also needs to be controlled.
4. Failure to use on time after baking: The PCB after baking must be used up within 5 days. If it is not processed within the time limit, it should be re-baked for 1 hour before going online again to prevent secondary moisture absorption.
5. Specific process node requirements: Before drilling and after lamination in PCB manufacturing, targeted baking is required to remove moisture that has seeped in during processing and eliminate internal stress. Some of the PCBS that have been returned from the warehouse for rework also need to be baked to restore their soldering performance.